
Agent Skills are a portable, open-standard format for packaging procedural knowledge so any AI agent can load domain expertise on demand—turning a general-purpose model into a specialist without re-explaining workflows every time.
Latest Blogs from Ylang Labs

Agent Skills are a portable, open-standard format for packaging procedural knowledge so any AI agent can load domain expertise on demand—turning a general-purpose model into a specialist without re-explaining workflows every time.
OpenClaw is an open-source AI agent platform that runs locally on your machine and works from the chat apps you already use.
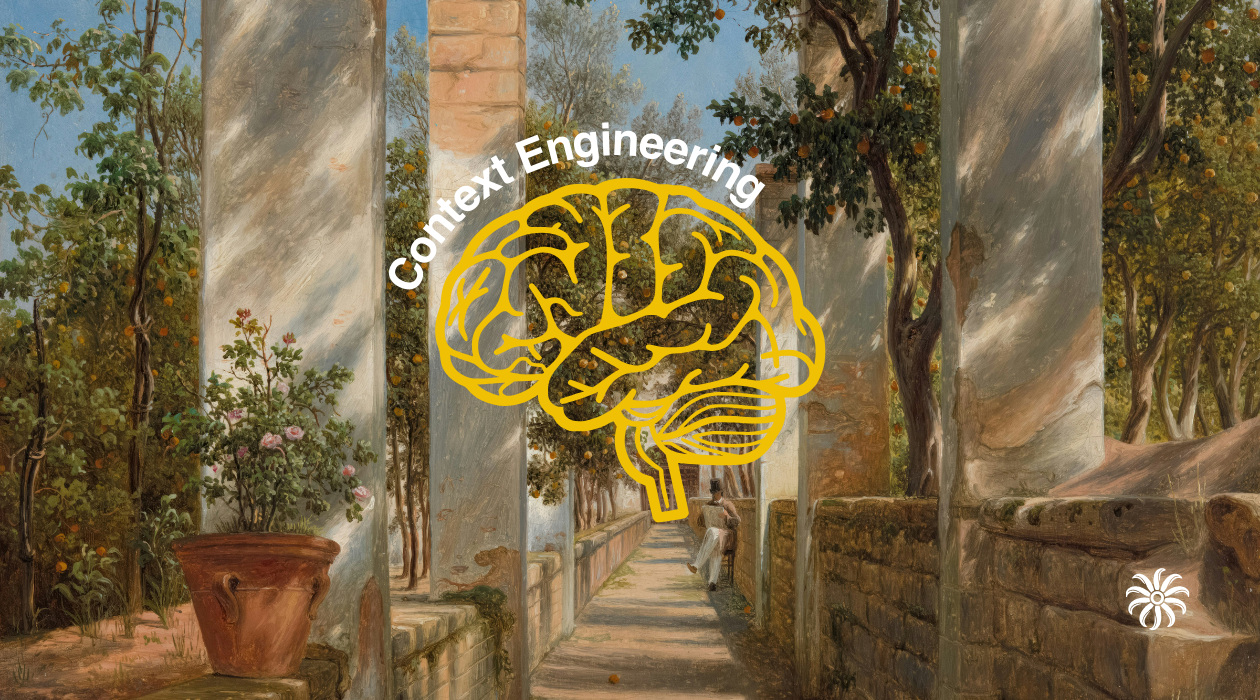
Prompt engineering describes the recipe; context engineering manages the kitchen. A technical playbook for the "mise en place" of AI agents: Write, Select, Compress, and Isolate.

Docling unlocks enterprise PDFs by converting them into a structured DoclingDocument with layout-aware pipelines, DocTags, and integrations that keep provenance intact for downstream AI and automation workflows.

Use Pydantic as your LLM contract: prompt with the actual schema, validate every boundary (including strict tool-call args), and turn ValidationErrors into structured retries rather than brittle prompt hacks; keep models provider-agnostic via thin wrappers (OpenAI structured outputs, Instructor, Pydantic AI), log like a flight recorder with prompts/model IDs/retry counts/versioned schemas, and evolve safely with explicit schema_version and migration validators, so rogue enums and bad JSON never touch production.
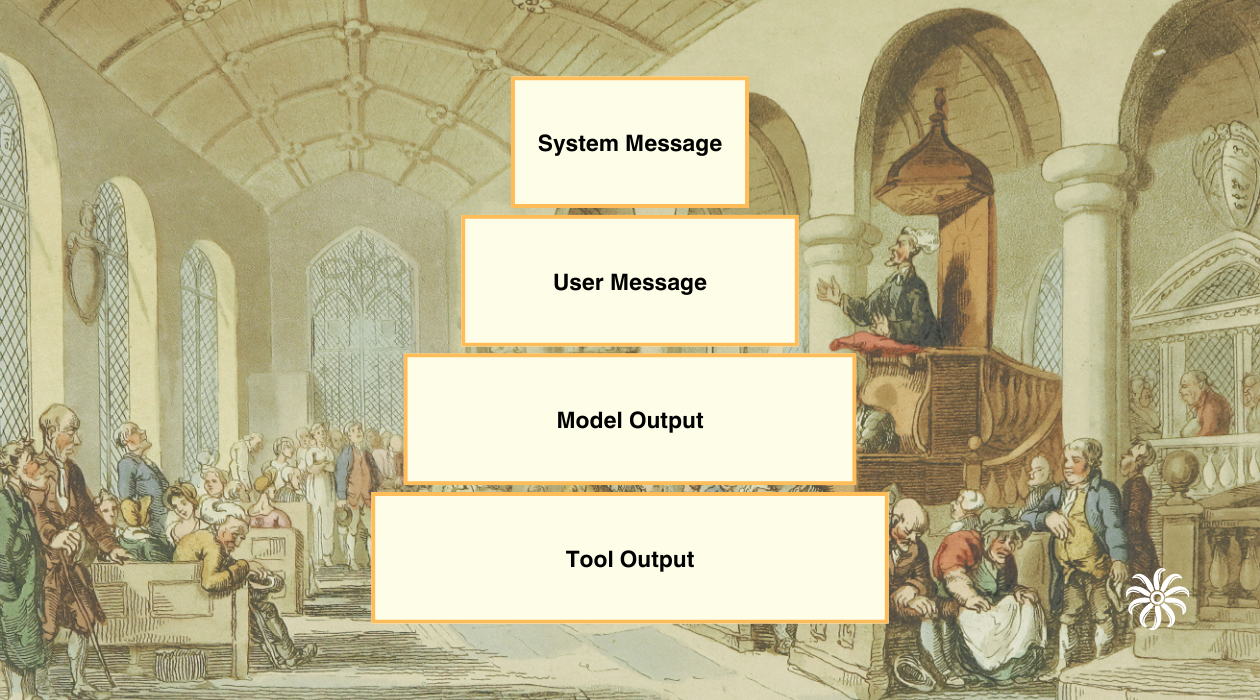
Some Large Language Models (LLMs) are vulnerable to security attacks because they treat all instructions equally. Implementing a clear instruction hierarchy—where developer instructions (highest priviledge) override user queries (medium priviledge), which override model outputs (lower priviledge), which override third-party content (lowest priviledge)—significantly improves security and enables more effective prompt engineering. OpenAI's research shows models trained with hierarchical instruction awareness demonstrate up to 63% better resistance to attacks while maintaining functionality. This approach not only mirrors traditional security models in operating systems and organizations, creating more trustworthy AI systems, but also provides prompt engineers with a more predictable framework for crafting reliable prompts that work as intended.
A comprehensive guide to evaluating large language models, covering fundamental metrics, open-ended evaluation techniques, LLM-as-a-Judge approaches, and practical guidance for implementing robust evaluation pipelines in real-world AI applications.
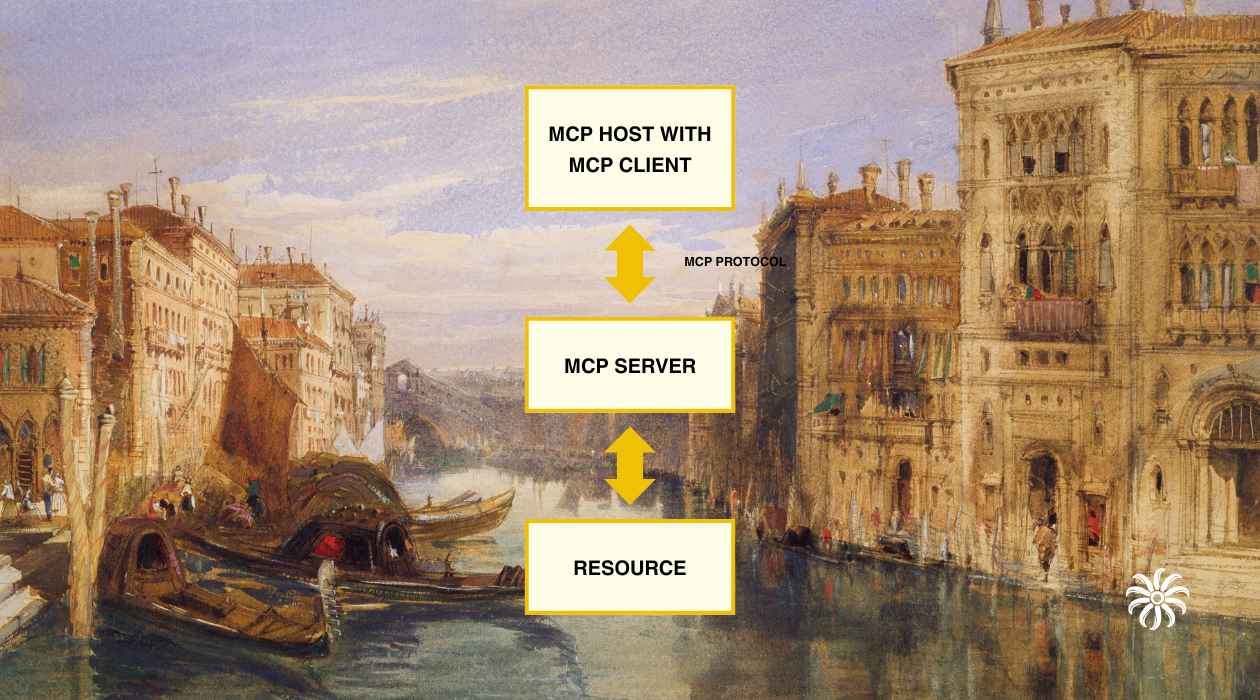
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is a standardized framework for integrating AI systems with diverse data sources and Applications. This post explores MCP’s architecture, core components, and best practices.
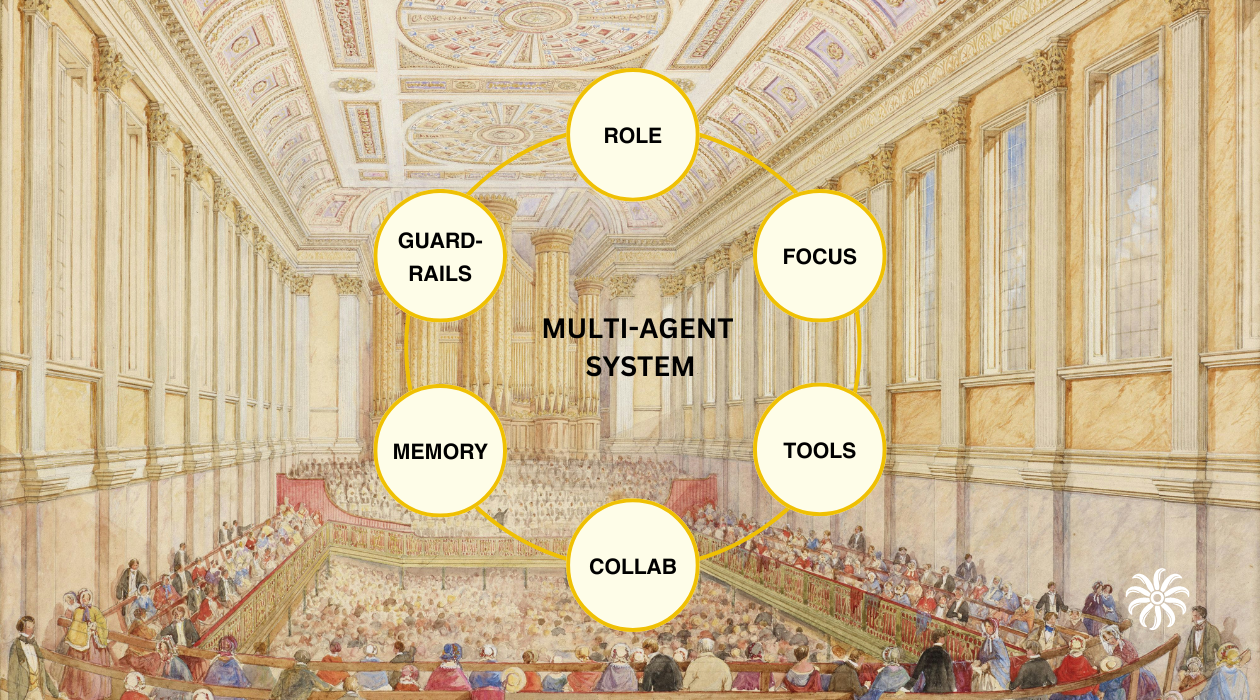
Explore the six essential elements that make multi-agent systems effective: Role Playing, Focus, Tools, Collaboration, Guardrails, and Memory. Learn how specialized agents working together can outperform single-agent solutions through clear roles, focused responsibilities, and powerful collaboration patterns.
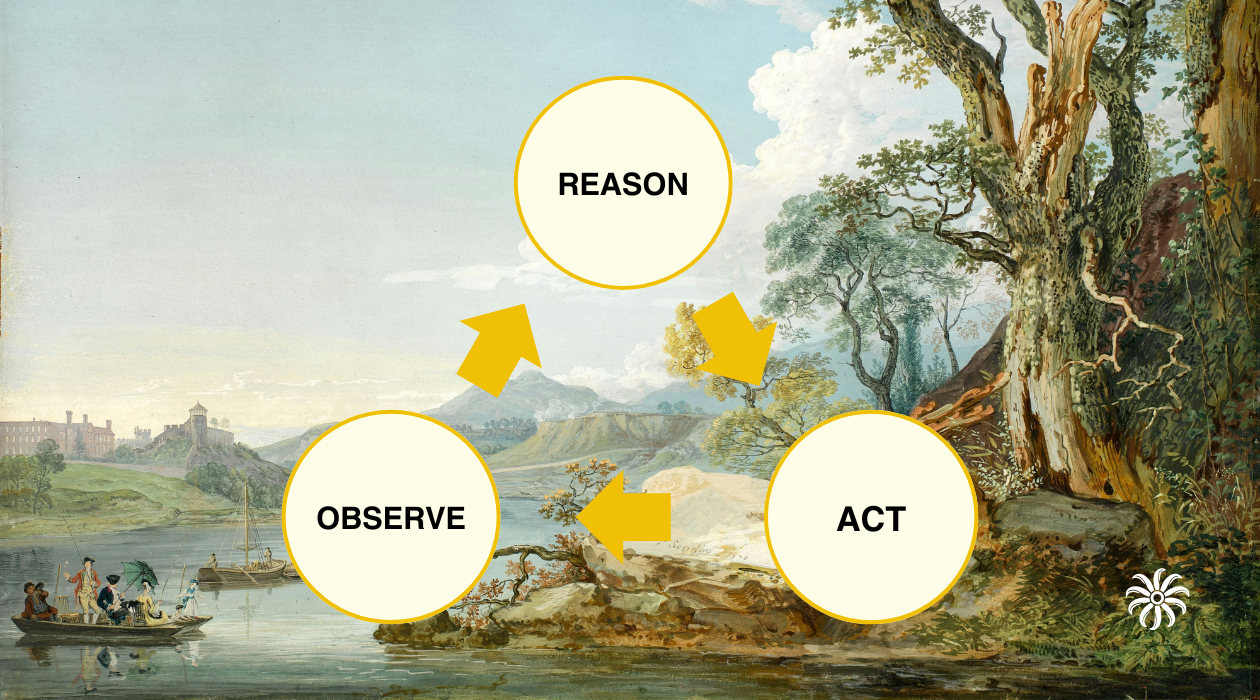
Explore ReAct, a framework where language models observe, reason, and act in a continuous cycle. Learn how this three-step process enables AI to gather information, think through problems step-by-step, and take concrete actions - creating more capable and reliable AI systems that can adapt their approach based on real-world feedback.
Showing page 1 of 2